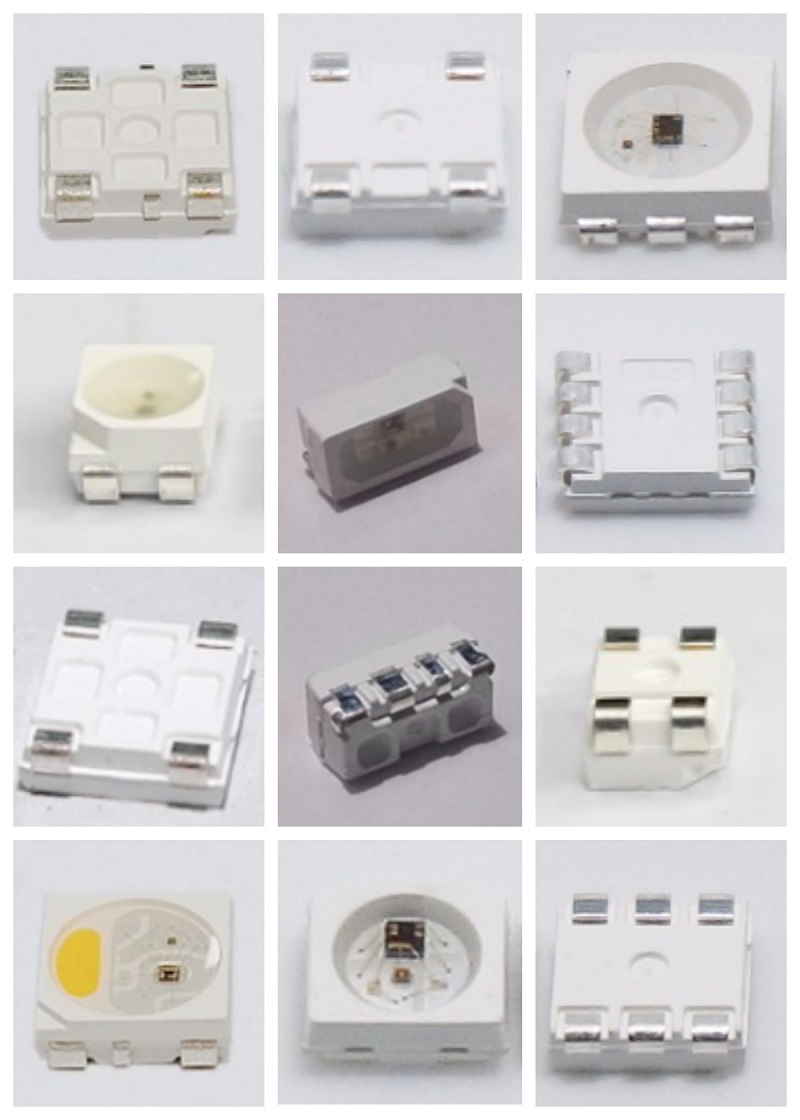
Best Guide to SMD LED with Built-in IC
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
When talking about the basic technology of the LED industry, what type do you think of first? Now let me reveal the answer. It is SMD LED with Built-in IC. It has become the basic technology of the optoelectronics industry, whose penetration rate in consumer electronics, automobiles, industrial displays, and other fields exceeds 75%. What an amazing proportion!
1. SMD LED with Built-in IC Definition
As a miniaturized optoelectronic device, SMD LED with (Built-in IC) integrates a Light-Emitting Diode (LED) with a driver/control integrated circuit (IC) within a surface-mountable chip-scale package. Being directly soldered onto PCBs via Surface Mount Technology (SMT) achieves a compact trifunctional design combining photonic emission, electronic driving, and intelligent control in one unified structure.
2. Types of SMD LED with Built-in IC
2.1 Classification by Communication Protocol
(1)Single-Wire Addressable: uses a single data line for control (e.g., daisy-chain configuration).
Examples: WS2812 smd led, WS2813 smd led, WS2801smd led, WS2811smd led, SK6812 smd led, SK9822 smd led, SK6818 smd led, SKC6812 smd led, SK6803 smd led, SK6805 smd led, SK6812 smd led, SK6805 smd led, SK6112 smd led, SK6112D smd led and so on.

(2)SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface): High-speed communication with separate clock and data lines for precise timing.
Examples: APA102, APA107, LPD8806

(3)I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit): Two-wire protocol for multi-device control on a shared bus.
Examples: PCA9685-driven modules
2.2 Classification by Color Capabilities
(1)RGB: Red, Green, and Blue LEDs with independent control for color mixing.
Applications: Decorative lighting, displays
(2)RGBW: adds a dedicated white LED for improved color accuracy and white light output.
Applications: Architectural lighting
(3)Tunable White:
Adjustable color temperature (e.g., 2700K–6500K) via dual white LEDs.
Applications: Human-centric lighting
(4)Single Color
Monochromatic LEDs with brightness control (e.g., white, red, blue).
Applications: Indicators, signage
2.3 Classification by Form Factor and Size
5050, 2835, 3535, 3528, 2427, 4020, 3512, 4246, 4236, 4242, 3725, EC3210R, 2222, EC10, CSP and so on.
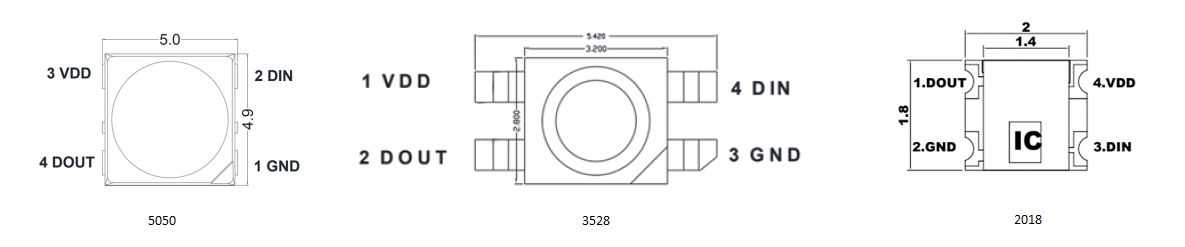
For example:
3528
Dimensions: 3.5 × 2.8 mm. Compact size, low power; ideal for dense installations.
5050
Dimensions: 5.0 × 5.0 mm. Larger size for higher brightness; common in RGB strips.
CSP (Chip-Scale Package)
Dimensions: <1.0 × 1.0 mm. Ultra-miniaturized for wearables, and AR/VR displays.
2.4 Classification by Application-Specific Features
(1)Automotive: AEC-Q102 certified; wide temperature range (-40°C to +125°C).
Use Cases: Headlights, interior lighting
(2)Industrial: High durability, IP67+ waterproofing, and surge protection.
Use Cases: Machine vision, outdoor lighting
(3)Medical: Flicker-free operation, high CRI (>90), and low EMI.
Use Cases: Surgical lighting, diagnostics
(4)Decorative: Addressable control, dynamic effects (e.g., chasing, gradients).
Use Cases: LED strips, stage lighting
2.5 Classification by Drive Current Specifications
(1)Low-Current (5–20mA):
– Operating current: 5–20mA.
– Voltage range: 3–5V DC.
– Ultra-low power consumption (<0.1W). – Miniaturized CSP/COB packaging. – Efficiency: >85% @ 5mA (ideal for battery-powered devices).
– Control: Single-wire protocol or I²C.
Applications: Ideal for low-power scenarios requiring strict energy efficiency, such as small indicator lights, and status LEDs in electronic devices (e.g., smart bracelets, remote controls).
Characteristics: Lower luminous intensity but sufficient for basic designated functions, minimizing power consumption.
Industry Standard: IEC 62384 (low-power efficiency)
(2)Mid-Current (50–150mA):
– Operating current: 50–150mA
– Voltage range: 12–24V DC
– Integrated PWM dimming (1–50kHz)
– Thermal resistance <5°C/W – Efficiency: >90% @ 12V input (ANSI C82.16 compliant).
– Thermal Design: Aluminum-core PCBs/ceramic substrates.
Applications: Commonly used in general indoor and decorative lighting.
Characteristics: It can balance brightness, luminous efficacy, and energy consumption, making it the most widely adopted category.
Industry Standard: EN 55015 (EMC compliance)
(3)High-Current (200mA–1A):
– Operating current: 200mA–1A
– Voltage range: 24–48V DC
– Multi-chip
– Active thermal management (TJ monitoring)
– Certifications: AEC-Q102 for automotive, UL 8750 for high-power LEDs.
– Driver Integration: Built-in buck/boost converters.
Applications: High-brightness applications and automotive headlights.
Characteristics: It can generate significant heat for its high current, necessitating robust thermal management for reliable operation and longevity.
Industry Standard: AEC-Q102 (Automotive), IEC 60601-2-41 (Medical)
2.6 Classification by Control Features
(1)Addressable: Individual LED control via data protocols (e.g., WS2812B).
Examples: LED matrices, and art installations.
(2)Non-Addressable: Group control with PWM dimming; simpler circuitry.
Examples: Backlighting, and basic indicators.
(3)Smart LEDs: IoT-enabled with Wi-Fi/Bluetooth and app integration (e.g., Philips Hue).
Examples: Smart home lighting.
2.7 Classification by Direction of Light Emission
(1)Front Emission:
The lamp beads are mounted on the PCB with their front side, and light is emitted in a direction perpendicular to the PCB, ensuring an all-around viewing angle of approximately 140°–160°.

(2)Side Emission:
The lamp beads are mounted on the PCB’s side, with light emitted from the beads’ side in a direction parallel to the PCB. Components like a light guide plate then alter the light direction. Since the circuit board blocks part of the light, ensuring only a single-side viewing angle, such screens typically feature higher transmittance.

3. SMD LED with Built-in IC Technical Features
(1)High Integration
Eliminates peripheral driver circuits required by conventional LEDs (e.g., MOSFETs, resistors, capacitors), reducing PCB footprint by over 60%.
Supports CSP (Chip Scale Package) or COB (Chip on Board) packaging, with dimensions as compact as 1.0×0.5mm (0402 form factor).
(2)Intelligent Control
Integrated IC enables:
Digital protocol control( I²C, SPI, single-wire interface).
Analog dimming( 0-10V linear regulation).
Advanced functionalities:
16-bit grayscale control (65,536 levels).
Dynamic lighting effects (breathing, gradient, strobe).
Real-time temperature compensation.
(3)Energy Efficiency & Reliability
Embedded protection mechanisms:
It uses (OVP/OCP/OTP) safeguards.
Its MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) exceeds 50,000 hours.
Power efficiency >90%, a 15-20% improvement over conventional solutions.
(4)Communication & Scalability
Cascading control architecture supports single-bus driving of hundreds of LEDs.
IoT protocol compatibility (DALI, Zigbee) for networked intelligent lighting systems.
4. SMD LED with Built-in IC Traditional Structure
(1)Light-Emitting Layer:
LED Chip: GaN-based blue LED chip (450nm wavelength) combined with YAG phosphor for white light emission (CCT range 2700K-6500K, ANSI C78.377 compliant).
Luminous Efficacy: Up to 180 lm/W (@350mA drive current, CCT 4000K, per IES LM-80 testing protocol).
(2)Control Layer:
Driver IC integrating critical circuits:
Constant current source (±1% accuracy, JEDEC JESD22-A101 qualified)
PWM dimming module (1kHz-50kHz frequency range, IEEE 1789 compliant)
Communication protocol decoder (I²C/SPI/single-wire interface, IEC 61131-2 standard) etc.
Protection Circuitry:
Triple-safeguard architecture:
Overvoltage Protection (OVP, 40V clamp voltage)
Overcurrent Protection (OCP, ±5% current threshold)
Thermal Shutdown (TSD, 150°C trigger point).
(3)Package Structure:
Substrate Material:
High-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic ( CTE 6.5 ppm/°C)
High-thermal-conductivity epoxy resin (>2.5 W/m·K, UL 94 V-0 flame-rated).
Optical Design:
Integrated micro-lens array (MLA) with:
Beam angle: 120° ±10% (IESNA LM-79 angular distribution)
Light uniformity: >90% (CIE 015:2018 spatial uniformity criteria).
5. SMD LED with Built-in IC Core Functions
(1)External Driver-Free Operation:
Built-in constant-current ICs directly match 3-5V power supplies, eliminating external driver circuits.
(2)Dynamic Lighting Effects:
RGB color-mixing ICs support 16.7 million colors with < 1 ms response time.
(3)Environment Adaptability:
Integrated light sensor ICs enable automatic brightness adjustment.
(4)High-Density Displays:
Ultra-compact packages with driver ICs enable pixel pitches as small as P0.4.
6. SMD LED with Built-in IC Applications
(1) It is widely used in Consumer Electronics such as flash in smartphones and smart wearable devices.
(2) It is commonly applied in Automotive Lighting like Matrix headlights and Cockpit atmosphere lights.
(3) It is largely used in Industrial Displays like Mini Led Backlight.
(4) It is also applied in IoT and Smart Cities like smart street lights.
7. SMD LED with Built-in IC Technical Advantages
(1)Circuit Complexity:
SMD LED with Built-in IC eliminates all external components through direct surface mounting (IPC-2221A compliant) and the BOM cost of it has been reduced by 45%, while conventional LED solutions require external driver circuits (e.g., buck converters, current-limiting resistors) occupying >30% of PCB area – a 68% reduction in board space utilization compared to discrete implementations.
(2)Control Precision:
SMD LED with Built-in IC features a digital dimming accuracy of ±0.5% (16-bit resolution), while conventional LED achieves an analog dimming accuracy of ±10%.
(3)Production Yield:
SMD LED with Built-in IC utilizes fully automated SMT (Surface Mount Technology) placement processes, whose yield rates >99.5%, achieving component mounting precision of ±0.025mm and throughput rates exceeding 80,000 CPH (components per hour), compliant with IPC-A-610 Class 3 standards.
Conventional LED products, however, are still predominantly manufactured using automated reflow soldering processes, with production yield rates of approximately 92% (IPC-A-610 Class 2 compliant), constrained by inherent limitations in component alignment accuracy (±0.1mm tolerance) and thermal profile control (J-STD-020 temperature curve adherence with ±5°C window).
Moreover, SMD LED with Built-in ICs utilize fully automated packaging, achieving a failure rate of <50ppm, compared to 300–500ppm for conventional LED assembly.
(4)Response Speed:
SMD LED with Built-in IC achieves chip-level control precision, delivering dimming response times <100ns (JESD22-A114 tested), whereas conventional LEDs remain constrained by external driver latency (~10ms) due to signal conversion delays and PCB trace parasitic effects (per IPC-2223 signal integrity guidelines).
(5)Reliability:
SMD LED with Built-in IC achieves chip-scale packaging integration with MTBF exceeding 100,000 hours (AEC-Q102 qualified for automotive headlamp applications), while conventional LED exhibits solder joint/wire aging vulnerabilities (MTBF ≈50,000 hours) due to intermetallic compound (IMC) growth at solder interfaces and polymer insulation degradation (per MIL-STD-883 Method 1015 accelerated life testing protocols).
(6)Development Cycle:
The development cycle of SMD LED with Built-in IC is shorter. SMD LED with Built-in IC enables plug-and-play deployment with software configuration accomplished within 1-2 days (Matter protocol compliant), whereas conventional LED implementations necessitate a hardware design and driver firmware development cycle spanning 6-8 weeks, as mandated by IEC 62304 for medical-grade system verification.
8. SMD LED with Built-in IC Manufacturers
There are plenty of SMD LED with (Built-in) IC manufacturers all over the world. The following list is the most representative.
Seoul Semiconductor
OSRAM
Nichia
Lumileds
Samsung LED
Worldsemi
Sanan Optoelectronics
HC SemiTek
Jufei Optoelectronics
BOE
…
9. SMD LED with Built-in IC FAQs
10. Summary
By achieving system-in-package (SiP) integration at the chip level, SMD LED with Built-in IC realizes a fully functional closed-loop system (power delivery, driving, and intelligent control) within a 1mm³ footprint. It has become a cornerstone of miniaturized, intelligent optoelectronic systems and will further penetrate cutting-edge fields like AR/VR and biomedical devices.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China