Melt a Strong Solder Joint in Circuit Card Assembly Manufacturing?
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
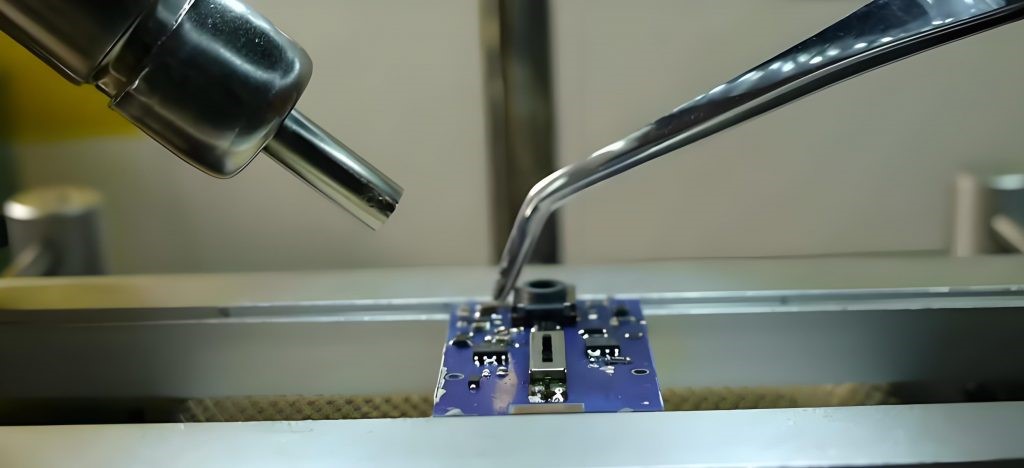
Here’s how to melt a solid solder junction. This method calls for flux, soldering iron, solder sucker, solder sucker braid.Leaded solder should set the soldering iron temperature between 300 and 350 degrees; lead-free solder should set it between 350 and 400 degrees. And then we should use a toothpick to pick up some flux and put it on the solder joint. The essential thing to do here is to melt the solder, heat is applied from the soldering iron. Remove the hot solder with a braid or solder sucker.
How Can Recalcitrant Solder Be Melted?
1. The melting of stubborn solder can be achieved through the use of appropriate solvents, heating methods, and specialized solvents or cleaners.
2. The composition of the solder determines the solvent used to achieve dissolution. Usually included are acetone, alcohol, acetic acid, toluene, and other solvents. It is done by applying a solvent, allowing it to stand for a minute or two, and cleaning it with a soft cloth.
3. Heat Methods Hot melt solder can be dissolved with heat. Use a heat gun or a specialist heat-fusing device to melt the solder.
4. Use of specialist solvents. Some solvents are tailored to specific types of solder , which are more effective.
What is the Appropriate Way to Remove Solder Excess from a Circuit Board?
Leftover solder after the manufacturing or repair of an electronic board may involve solder films or a few blisters. The residues are supposed to be removed to let the board perform as it’s supposed to under said normal use. Common cleaning techniques are discussed as follows;
1. Method 1
• Soak the board in acetone for around 10 minutes.
• Wipe up whatever residues left after cleaning the board with a 95% alcohol solution.
• Carefully remove with a soft-bristle brush.
• After cleaning, the board can be dried with absorbent material like cotton.
• Utilize a solder sucker to create soldering holes with a needle, then insert and rotate the soldering iron after heating. Alternatively, you can shake the printed board after heating to remove residual tin.
2. Method 2
• Melt the solder connection once more after shaking off the solder with the soldering iron. You should repeat this method multiple times.
• A tiny piece of multistranded wire should next be found, dipped in rosin, and melted with the solder joint. While the wire is still hot, remove it and scrape off any extra solder.
• Next, find a small piece of multi-stranded wire, dip it into rosin, and melt it together with the solder joint. Remove the wire while it is still hot and remove the excess solder.
• For larger areas, consider using a specialized hot air gun or tin furnace.
3. Method 3- Ultrasonic Cleaning
• This method is to soak the board in acetone solution for about 10 minutes.
• Next, the PCB board should be placed into an anhydrous ethanol bottle and placed inside an ultrasonic cleaning tank for approximately 5 minutes.
The temperature specification of various soldering techniques
Manual soldering- The range of temperature required for manual soldering typically ranges from about 300° to 350°. Manual solder-Usually between 300°C and 350°C. Solder the wire in this range.
Temperature Specifications for Various Soldering Techniques
1. Manual Solder
• The range of temperature required for manual soldering typically ranges from about 300° to 350°. Manual solder-Usually between 300°C and 350°C. Solder the wire in this range. It guarantees enough wetness and melts rapidly.
• Time Required Depending on the wave’s height and the conveyor belt’s speed, the process takes three to five seconds.
2. Wave Solder
• Usually accomplished at temperatures ranging from 245°C to 265°C. The goal of this temperature range is to protect the solder from damage during wave soldering. This temperature is crucial to make sure the wave sufficiently moistens the solder and adhesives it to the pads and component pins of the PCB board.
• Time Needed The procedure takes between three and five seconds, depending on the speed of the conveyor belt and the height of the wave.
3. Reflow Solder
• Usually, the temperature ranges between 245°C and 265°C. The temperature profile consists of a preheating zone between 100°C and 150°C, an insulating zone between 150°C and 180°C, a reflow zone between 210°C and 240°C, and a cooling zone.
• Time requirements usually take three to six minutes to complete the reflow procedure.
Which Kinds of PCB Solder joints are there?
1. Surface Mount Solder Joints. This type of connection is used to solder surface-mount components. To bind the component to the PCB surface, solder paste is heated in hot air furnaces and other equipment.
2. For plug-in components, plug-in solder joints are appropriate. Manual soldering or wave soldering must be employed to connect the component pins to the PCB.
3. Components on double-sided or multi-layered electronic boards are soldered with through-hole solder connections. Wave soldering or other methods must be used to secure the component pins once they have been passed through the printed circuit card.
What occurs if the solder joint becomes too hot?
1. Performance degradation Because the electrical components on the circuit board are temperature sensitive, overheating may cause component performance to decline.
2. Reduced Life Electronic components age faster at hot temperatures, shortening their lifespan.
3. Thermal Expansion and Stress The circuit card and its components expand in reaction to temperature changes, and overheating can cause solder connections to flex, shatter, or peel.
What are the recommended temperatures for working with PCBs?
The maximum temperature at which an electronic card can withstand melting solder is 280 degrees Celsius. The solder will melt at this temperature without permanently harming the electronic card. The constructed printed circuit card could be harmed, though, if the temperature rises above this range.
Control of PCB Temperature While Soldering
1. Preheat Temperature. To reduce the impact of thermal stress on the components, circuit boards are typically preheated to 80°C to 120°C before soldering.
2. Soldering Temperature. To ensure that the solder melt completely wets the soldered surface, the solder’s temperature must rise above its melting point during the soldering operation.3. Peak Temperature. Certain parts of the electronic boards may experience peak temperatures during soldering that are higher than the soldering temperature.
We have extensive experience in PCB soldering as a professional complete circuit card manufacturer, and we have highly qualified staff members who know how to use a soldering iron, hot air gun, and other instruments. To guarantee flawless solder joint quality, we also specialize in precision motherboard soldering joints and connecting points on big industrial printed circuit cards.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China