The Complete Guide to Printed Circuit Board Assembly
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
PCB Assembly is the cornerstone of electronic devices. Chances are that a PCB powers your smartphone, laptop or tablet. This article dives into the fascinating world PCB Assembly and breaks down complex concepts in a language that everyone can understand. This guide will provide you with all the necessary information, whether you are new to this topic or just want to review it.
1. PCB Assembly Overview
Anyone interested in electronics should understand this process because it is essential to the production of electronic devices.
PCB Assembly can be compared to adding organs and muscle to an electronic device. This process is what brings a circuit’s bare bones to life.
2. What Is a Printed Circuit Board (PCB)?
A Printed Circuit Board is a board that has been produced with a non-conductive substance. It provides a path and actual support for electrical components. These boards are usually made from fiberglass, composite epoxy or other laminate materials.
What Is the Function of PCBs?
These pathways, which are usually in the form or copper tracks, connect components such as resistors and capacitors. These “streets” are what guide the electrical flow to the various parts of the board. This allows the gadget to perform its intended function.
3. PCB Assemblies Types
PCB assemblies come in a variety of types, with each type being suited to a different application. The choice of assembly type is based on factors such as the complexity of the circuit, size of parts and intended use of the final result.
PCB Assembly with a Single Side
Single-sided PCB Assembly is a type of assembly where components are only attached to one side of the board. This type of assembly can be used to make low-cost electronic devices like radios and calculators.
Double Sided PCB Assembly
Double-sided printed circuit boards allow for more complex circuits to be constructed in a smaller space. Components are mounted on both sides. Consumer electronics, such as smartphones and laptops, often use this type.
Multilayer PCB Assembly
Multilayer Assembly is made up of several layers of PCBs, stacked one on top of the other with an insulating layer in between. This type of assembly can be found in high-performance electronic equipment such as servers or telecommunications gear, where functionality and space are important.
4. PCB Assembly Key Components
PCB Assembly is a complex process that involves many components. Understanding these components is essential for understanding the complexity and usefulness of assembly.
Resistors
Resistors are components that provide resistance to electrical flow. They are used to protect other parts and ensure the proper working of the circuit.
Capacitors
Capacitors are used to store and deliver electrical energy. They are essential for smoothing voltage fluctuations and supplying power to different parts of the circuit.
Diodes
They block electrical impulses by allowing current to only flow in one direction. Diodes are used to protect electrical circuits against damage.
Transistors
Transistors are the fundamental component of modern electronics. Transistors are essential to the operation of nearly every electronic device. They can switch or amplify electrical signals.
Integrated Circuits
A reduced electronic circuit, an integrated circuit (IC), is made up of several components. ICs can be found in virtually all electronic gadgets that are advanced, including PCs and cell phones.
5. PCB Assembly Process
Each step is crucial to a reliable and functional circuit. Below are the most important step.
Circuit Board Design
This interaction begins with the planning of PCB formats using specific software. This plan includes the arrangement of components, the steering of paths, and other fundamental details.
Solder Paste Application
During this phase, the solder paste will be applied to the areas where the components are going to be installed. This paste is made up of flux and solder balls to help with the soldering.
Component Positioning
Component Positioning After the solder paste has been applied, the components are placed on the board. Automated machines are used to position components according to the design.
Reflow Soldering
Reflow Soldering The board is placed into a reflow-oven where the paste melts, bonding the parts to board.
Inspection
The PCB is then tested and reviewed to ensure that all components are correctly positioned, and the circuit functions as intended.
6. SMT
Surface Mount Technology allows components to be mounted directly on the PCB surface, as opposed to through holes. Surface Mount Technology (SMT). Due to its efficiency, and ability to handle small components SMT is used most often in modern PCB assembly.
Benefits of SMT
• Reduced Plans: SMT believes that more parts will be placed in a smaller region, resulting in minimal and lightweight plans.
• Automation by Assembly: SMT is highly automated and speeds up production while reducing the risk of human error.
• Economical: Due to its efficiency, SMT assembly is often more cost-effective.
7. Through-Hole Technology
Through-hole Technology (THT) is an older method of assembling PCBs, in which components are soldered on the other side of the board once they have been inserted into the holes drilled in it.
Even though it is becoming less popular, THT is still being used in certain applications that require mechanical strength.
Benefits of THT
• Stronger connections: The THT components are physically attached to the board and therefore more resistant to mechanical stresses.
• Power Components are Reliable: THT connections are often used for high-power components requiring more robust connections.
8. Mixed Technology PCB Assembly
This method is used when the design needs both surface mount and machine technology.
Mixed Technology
• Complex Circuits Mixed Technology is ideal for circuits that require small components (SMT), as well as robust connections (THT).
• Individual Designs This method allows for more flexibility in custom design and can accommodate many different component sizes and types.
9. Cost of Good Security
To maintain the dependability of the final product, it is necessary to check that each board works correctly and without errors.
Testing Methods
• Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): This technique uses cameras to look for PCB flaws, such as soldering issues or missing components.
• Inspection by X-Ray: The X-rays can be used to inspect the internal structure of a PCB and check for defects that are not visible using other methods.
• Functional Test: After assembly, the PCB is tested in normal conditions.
10. PCB Assembly: Challenges and Opportunities
PCB Assembly can be a complicated process, with many challenges to overcome in order to produce boards of high quality.
Miniaturization
As devices get smaller, PCB components must shrink. The miniaturization of devices poses challenges to both the design and assembling processes.
Heat Management
PCB assembly is a complex process that requires careful attention to heat, especially in circuits with high power. Overheating may damage the board components and reduce its lifespan.
Material Select
Material selection The PCBs’ durability, performance and cost-effectiveness all depend on the material selected. The wrong material can lead to delamination and poor performance.
11. PCB Assembly Advancements
New technologies and methods for PCB Assembly PCB Assembly constantly develops new technologies and techniques to improve functionality, reduce cost, and increase efficiency.
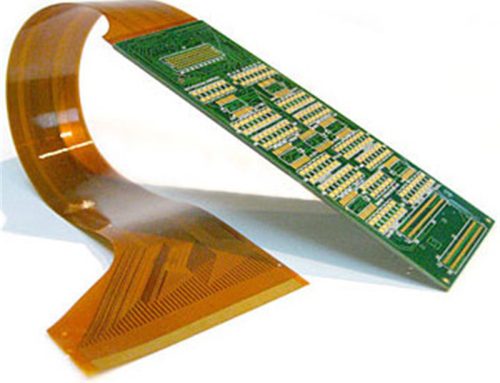
Flexible PCBs
Flexible Circuit Boards can be produced with adaptable materials that allow them to be twisted and collapsed. This adaptability allows for new design and applications, especially in wearable electronics.
3D Printing
3D printing has been considered as a method to produce PCBs because it can be used for rapid prototypes and individual designs.
Automated Inspection
Automated Inspection Technologies, such as machine learning algorithms, improve the speed and accuracy in quality control procedures.
12. PCB Assembly: Applications
PCB Assembly has many applications including consumer electronics and industrial machinery. Below are the most common uses. The most common uses are listed below.
Consumer Electronics
PCBs are required for the majority of consumer electronics, such as tablets, TVs, and phones. These devices are built on PCBs, which form the basis of their operation.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, PCBs are used in engine control systems as well as entertainment systems. In this industry, the PCBs’ dependability and durability is crucial.
Medical Devices
Medical devices rely heavily on PCB Assembly to operate, from simple diagnostic equipment to complex imaging gear. Precision and dependability of the PCB are essential in this industry.
Telecommunications
The use of network equipment, such as servers, switches and routers, by the telecommunications sector, is dependent on PCB assembly. These devices must be fast and efficient to maintain communication networks.
13. Selecting the Right PCB Manufacturer
Keep the following in mind:
Expertise and Knowledge
Know-how and skills Choose a manufacturer who has experience in your application and has a successful track record. Experienced manufacturers are more likely than others to produce high-quality boards.
Customization Options
Options for Customization When you require unique designs or materials, find a manufacturer who offers customization options. Flexibility is key to meeting your needs.
14. Environmental Impact of PCB Assembly
PCB assembly, like many other manufacturing processes has an impact on the environment. Understanding and mitigating this impact is crucial for the production of sustainable products.
Waste Management
Waste PCB Assembly produces waste that includes hazardous chemicals, defective boards and unused components. To minimize the harm caused to the environment, it is essential that waste management practices such as recycling and secure disposal be followed.
Energy Consumption
PCB Assembly consumes energy in particular during steps such as reflow soldering. Reduced energy consumption can be achieved by using efficient equipment and processes.
Eco-Friendly Material
The use of eco-friendly materials, such as recyclable substrates and lead-free solder, in PCB Assembly can reduce the impact on the environment.
15. Future Trends for PCB Assembly
PCB Assembly has a bright future, as several trends are shaping the industry.
Miniaturization & Integration
As devices become smaller and more integrated, the demand for PCBs that are small and multifunctional will continue to increase. This trend drives advancements in design, materials, and assembly techniques.
Sustainability
Greener PCB Assembly is being developed as a result of the push towards sustainability. This includes using biodegradable material and reducing energy usage.
AI Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are increasingly being integrated into PCB Assembly, especially in areas such as design optimization and quality assurance.
16. Last Words
The PCB assembly process, or printed circuit board assembly as it is also called, is the basis of modern electronics. From the initial design to the final test, every step is crucial for a reliable and functional circuit. PCB Assembly is expected to continue developing in line with the technological advances, opening new avenues for efficiency and innovation.
Anyone interested in electronics – whether they are a student, professional or hobbyist – must understand PCB Assembly. This guide simplifies complex concepts to make PCB Assembly more accessible.
17. FAQs
1. What is the difference between PCB Assembly and PCB Assembly?
PCB Assembly is the process of connecting components to the PCB in order to create a circuit.
2. What are the main types of PCB Assemblys?
PCB Assembly is divided into three basic types: Single-Sided Assembly, Two-Sided Assembly, and Multi-Facet Assembly. Each type has its own advantages based on complexity and size.
3. Why is PCB Assembly Quality Control Important?
The quality control ensures that the PCB collected is free of imperfections and is working accurately. This is crucial for dependability and the final outcome.
4. Surface Mount Technology (SMT)?
Surface Mount Technology is a method for mounting components directly on the surface of a PCB. It allows for more efficient and reduced plans.
5. How does PCB Assembly affect the environment?
PCB Assembly has a natural effect that is enhanced by utilizing eco-friendly materials, energy efficient cycles and squandering the executives.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China