15 Basic Components of PCB
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
15 basic components of PCB
If you do not know about electronic circuit board, you should be aware of PCB. But why do you need to know this, you may ask?
These circuit boards are used in all the electronic products we know, and their importance is self-evident. However, for beginners in electronics, they can often seem quite mysterious due to the many different parts on the circuit board, which look and function differently.
This article aims to introduce beginners to 15 common parts of circuit boards and their functions.
These parts include:
• Resistors
• Capacitors
• Light Emitting Diodes
• Transistors
• Inductors
• Diodes
• Integrated Circuits
• Transformers
• Sensors
• Potentiometers
• Crystal Oscillators
• Switches and Relays
• Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs)
• Passive Device Guides
• Wires
1. Resistors
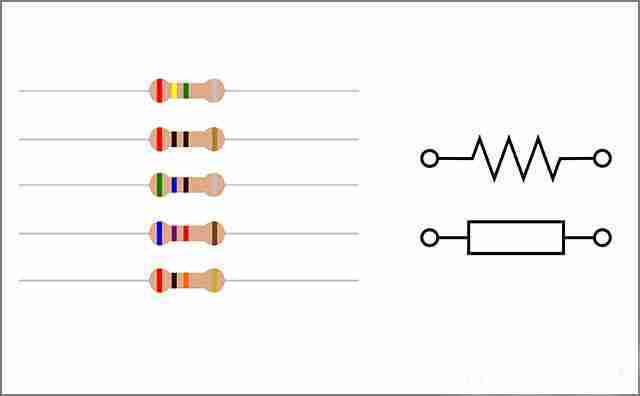
First, let us talk about resistors. Resistors are an integral component of PCBs and are one of the simplest components to understand. Their main function is to actively dissipate or disperse the current by converting it into heat, thereby reducing the current flowing through the PCB. Resistors are made of a variety of materials and come in a variety of types. For beginners or hobbyists, a typical resistor usually has two ends and leads, and its body will be marked with colored rings. These rings are the code for the resistance value.
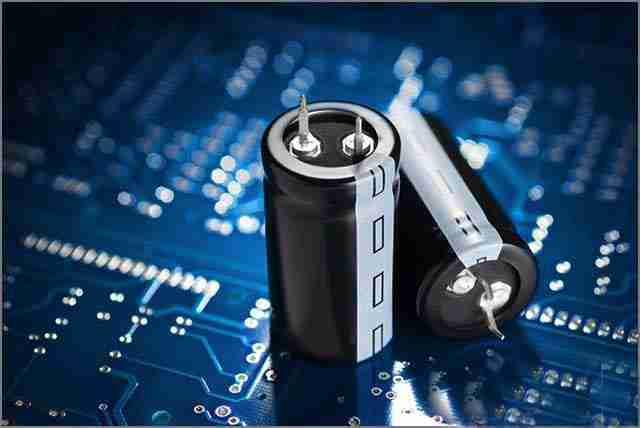
2. Capacitors
In addition to resistors, capacitors are also one of the common components on printed circuit boards. Usually, there are more resistors than capacitors. The function of capacitors is to temporarily store electronic charges and release these charges when power is needed at any part of the circuit.
Capacitors achieve their function by collecting opposite charges between two conductive layers separated by a dielectric or insulating material. The main characteristics of a capacitor depend on its dielectric or conductive material. Although traditional capacitors are radial in shape, they are composed of two axial leads, and some capacitors may look similar to axial resistors.
3. LED
In electronics, especially for beginners, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are components that are often encountered. The symbol of the LED is based on the standard graphic of a diode, with two arrows attached to indicate the emission of light, hence the name LED, or light-emitting diode. LED technology is widely used on many occasions, including artistic lighting, outdoor lighting, and night lighting.
As a semiconductor device, LED converts current into light energy when it passes through. When electrons and holes move in the material and combine, they form a complete atomic structure and release photons, the energy of the light.
4. Transistor
Transistors are considered an essential building block in modern electronics and are found in billions of units on integrated circuit chips. Transistors primarily act as electronic switches and amplifiers. Although there are two types of transistors, PNP and NPN, bipolar transistors are the most common due to their ubiquity. Bipolar transistors have three pins: the collector, the base, and the emitter. There is also a type of transistor called a field effect transistor (FET), which uses an electric field to control the activation state of another circuit.
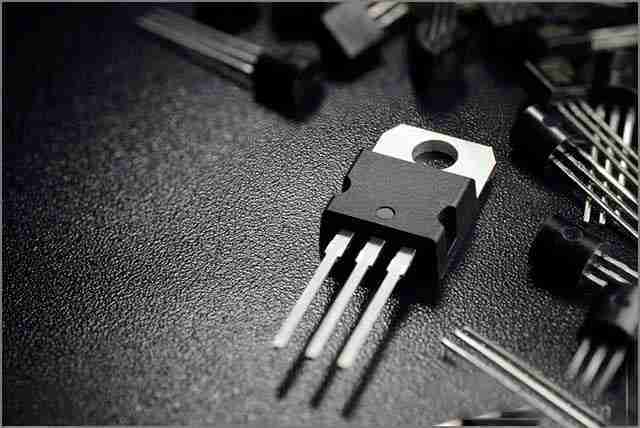

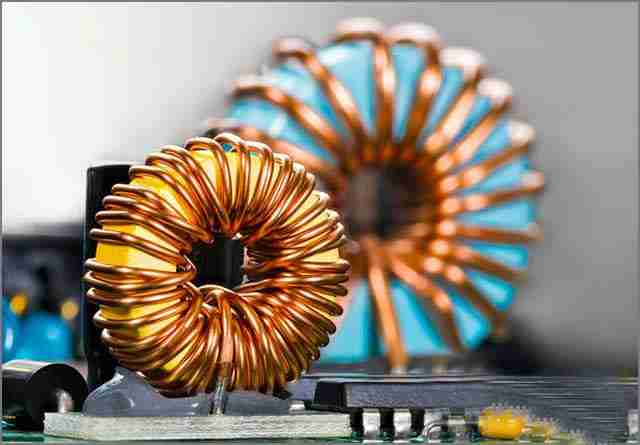
5. Inductor
In electronic engineering, inductors, capacitors, and resistors are the basic components that make up linear passive circuits. Inductors are similar to capacitors in that they can store energy, but they store it in the form of a magnetic field. This energy is generated at once when current passes through the inductor. The basic structure of an inductor can be simply regarded as a coil of wire, and the inductance of an inductor is proportional to the number of its windings. The more windings, the stronger the magnetic field generated, thus the higher the inductance value.
The main application of inductors is to shield or filter specific signals. For example, in television equipment, inductors can be used to suppress interference signals, and in AC power supplies, inductors are often used in conjunction with capacitors to adjust and control signals, especially in switching power supply technology. It plays a key role.

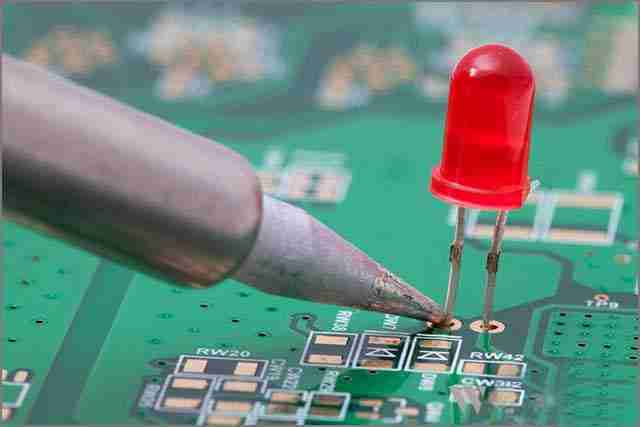
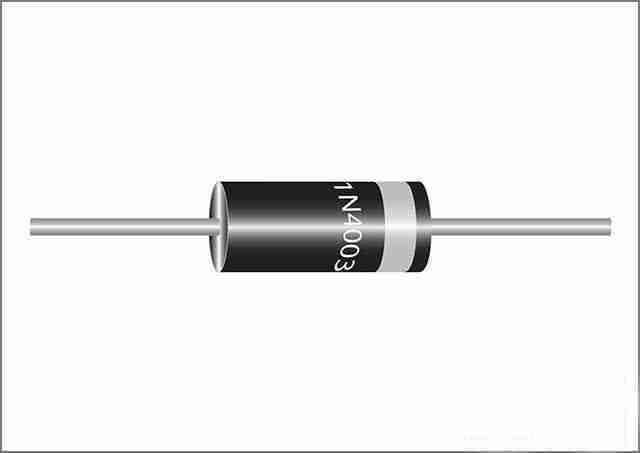
6. Diode
As an electronic component, a diode functions like a one-way street, allowing current to flow in only one direction. Specifically, current can only flow from the anode to the cathode. The diode achieves this characteristic by presenting a low resistance when conducting in the forward direction and a high resistance when blocking in the reverse direction. This characteristic effectively prevents the current from flowing in the wrong path, which may cause damage.
Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are widely used by beginners to achieve lighting functions because they are easy to use. However, before using LEDs, it is crucial to understand their directionality to avoid them not emitting light properly.
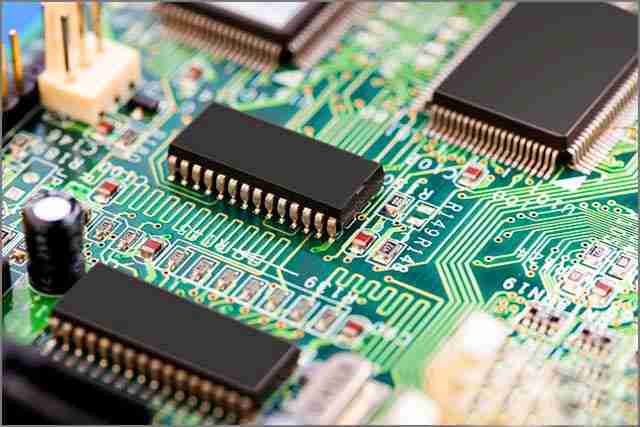
7. Integrated Circuits
Integrated circuits, also known as microcircuits, are a series of electronic components and circuits miniaturized and integrated into a wafer of semiconductor material. This highly integrated feature allows a large number of components to be effectively integrated into a single integrated circuit chip, giving rise to computers with excellent performance, the first calculators, and powerful supercomputers. Integrated circuits play a central role in printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Typically, integrated circuits are packaged in black casings made of plastic materials, which may come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The external contacts of the integrated circuit, such as leads and contact pads, are visible and extend from the package to connect to external devices.

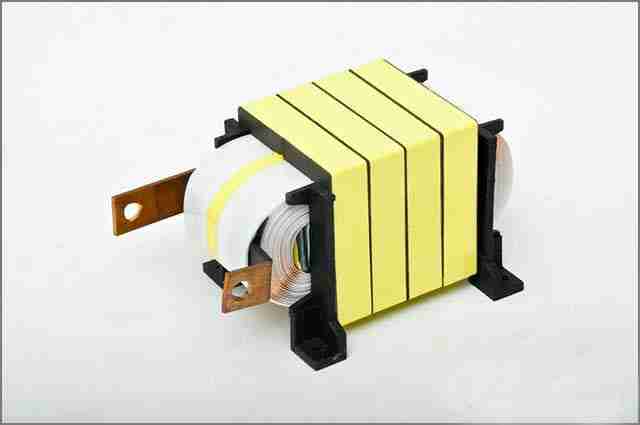
8. Transformer
The key purpose of a transformer is to ensure the efficient transfer of electrical energy from one circuit to another. This process should be achieved whether the voltage is stepped up or down. In short, a transformer has the function of voltage conversion. Similar to the inductor, a transformer has a flexible iron core with at least two windings.
The transfer of energy occurs between the primary coil and the secondary coil. You may have seen many industrial transformers installed on utility poles. Their function is to reduce the high voltage from the overhead transmission lines to a low voltage suitable for domestic use.

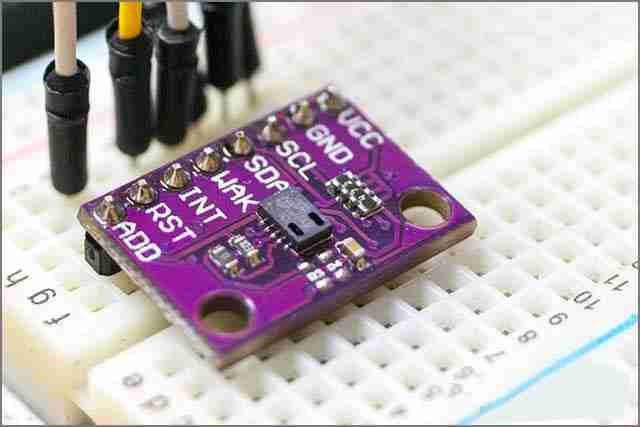
9. Sensors
These circuit components detect any changes in the environment and respond quickly by generating corresponding electrical signals. Sensors work by converting the energy of physical phenomena into electrical energy, or in short, converting the form of energy. Most sensors can respond to a variety of environmental stimuli, including light, humidity, air quality, motion, and sound.
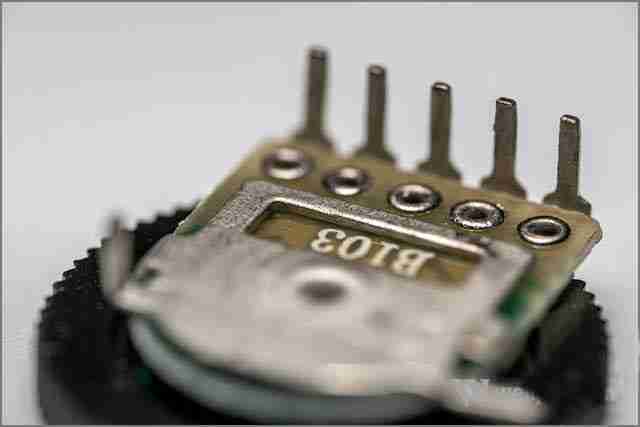
10. Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a form of variable resistor. Potentiometers are mainly divided into two types: linear and rotary. When the knob of the rotary potentiometer is turned, the resistance value changes accordingly due to the movement of the slider contact on the semicircular resistor body. A typical application example of a rotary potentiometer is a radio volume control knob. The working principle of the potentiometer is the same, except that the change in resistance value is achieved by the linear movement of the slider contact on the resistor body.
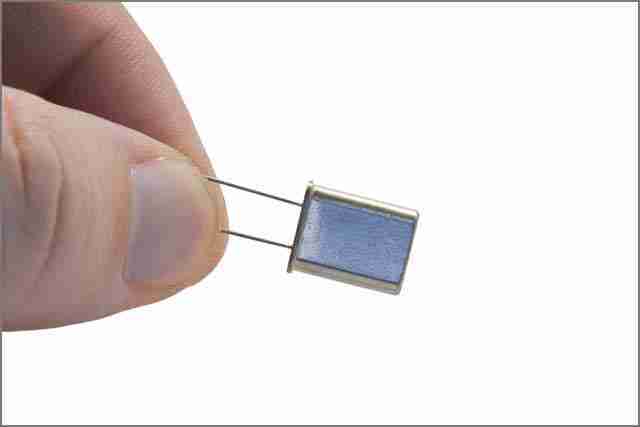
11. Crystal Oscillator
Crystal oscillators on electronic circuit boards do provide clock signals for many circuits that require stable timing and precise components. Crystal oscillators physically excite the vibration of piezoelectric materials by generating periodic electronic signals.
Compared with other timing methods, crystal oscillators can vibrate stably at a specific frequency and have the advantages of being economical and small in size. Based on these characteristics, crystal oscillators are mainly used in precision timing and are widely used in almost all quartz watches.
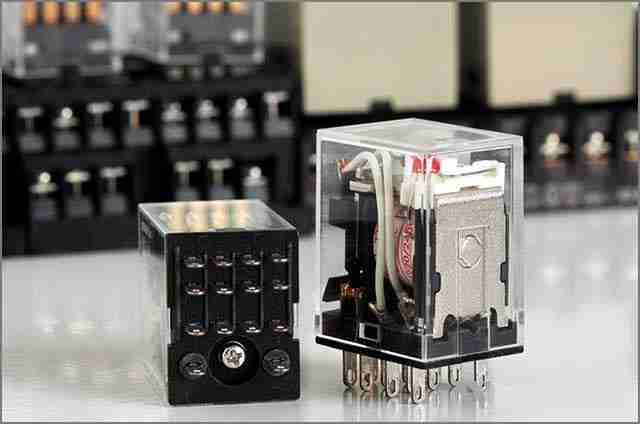
12. Switches and relays
Switches and relays play a vital role in electronic circuits, although they are often overlooked. Switches, as key components that control the flows of the current in circuits, achieve their functions by switching between closed and open states. Switches come in various forms, including rotary, joystick, push-button, and key-operated. Relays are switching devices that use electromagnetic coils to operate. They not only perform the function of switches but also convert weak current signals into larger current outputs, thereby amplifying current.

13. Silicon controlled rectifier (SCR)
Thyristors, also known as thyristors, function similarly to diodes and transistors. Designing and building a thyristor (SCR) requires two transistors to work together. The device has three leads and four layers of silicon material. Unlike devices with only three layers of silicon material, its main function is to act as a switch rather than an amplifier. Another significant difference is that only a single pulse is required to activate the switch. Thyristor rectifiers are particularly suitable for applications requiring large amounts of electrical energy.
![]()
14. Passive Components Guide
When discussing electronic circuit boards, we often come across the term “passive components”. Passive components are an integral part of the manufacturing process of electronic circuit boards. They are those components that do not generate energy in the electronic circuit, although they can consume or store energy without the need for an external power supply.
Passive components are mainly divided into two categories: lossless and dissipative. Dissipative components cannot absorb energy from the external circuit, while lossless components do not have any input or output flow of energy. Typical representatives of passive components include inductors and diodes.
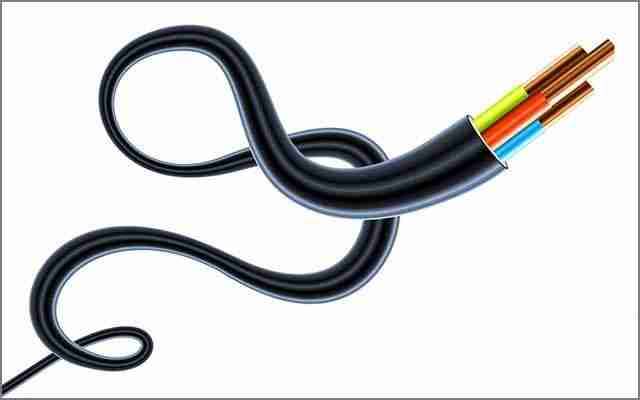
15. Wires
Wires are mainly used to connect various electronic devices to transfer electrical energy from one power source to another. Although some electronic cables are made of aluminum or other materials, the vast majority of cables are still made of copper as the main material. However, the choice of cable depends on its application requirements. There are many types of electronic cables on the market, including flat cables, shielded cables, hookup cables, and RF coaxial feeders, each suitable for specific purposes.
Conclusion
Assypcb SMT processing: By now, you must have known about the common electronic components on electronic circuit boards.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China