How to Choose the Best Materials for Your Designs of Flexible PCB
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
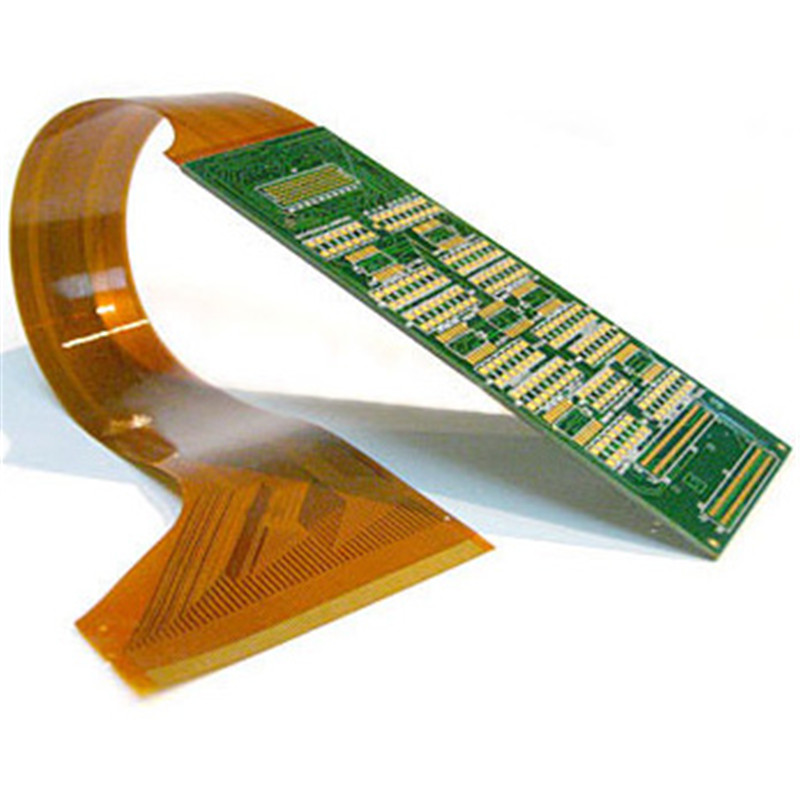
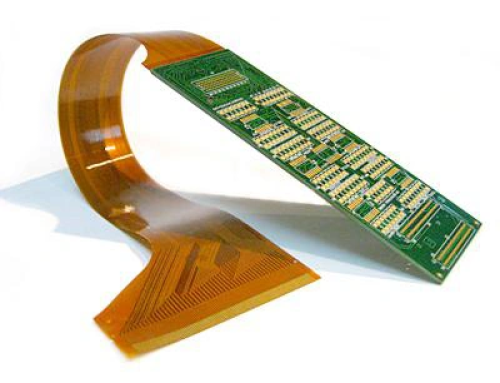
Flexible printed circuit board (Flexible PCB) has revolutionized the electronics sector. We can now pack the circuit into a small space using a highly compact, lightweight, and flexible form factor. FPCs are used in a wide range of applications, including medical implants, wearable technology, and aeronautical systems. These circuits are based on materials that provide the perfect balance between mechanical flexibility and electrical performance.
When developing a Flex PCB, selecting the appropriate substrates, coatings, and adhesives is crucial. FPC design is still lacking. We are experts in rigid PCBs, and we have plenty of information. The circuit’s base is made of materials that have a direct impact on its dependability. The most often used materials are examined in this article, along with recommendations for selecting the best material for your application.
1. Substrate materials: the foundation of flexibility
The substrate is a base layer for a Flex PCB. It’s the “flex” of flex circuits. The substrate supports the copper traces and is a major factor in determining mechanical and thermal properties. Three main types of materials are used to make FPCs.
- Polyimide (PI): the Industry Standard
- Polyester (PET): a cost-effective alternative
- PTFE (Teflon) and LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer).
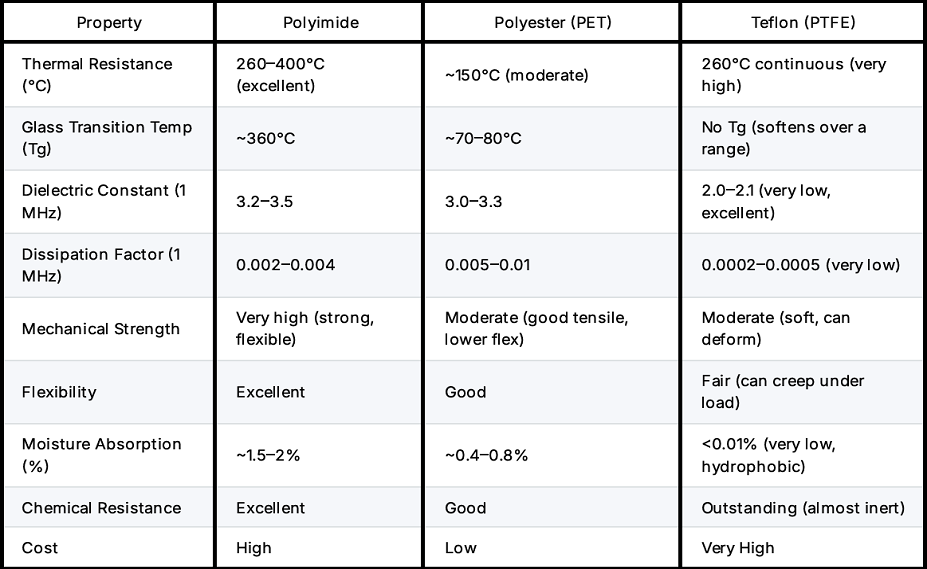
1.1 Polyimide(PI)
Polyamide in FPC plays the same role as FR4 dominates rigid PCB and is an industry standard in low-cost and hobby PCB manufacture. Because of its dielectric qualities, flexibility, and resistance to heat, polyimide is the most often used substrate material for Flex PCBs. It is mainly used in low-frequency consumer electronics. Below are some of its key benefits:
⦁ High temperature tolerance (up to 260°C in the short term)
⦁ Excellent dimensional stability
⦁ Chemical and solvent resistance

1.2 Polyethylene (PET)
Polyester is less expensive than PI, and it’s better for applications that aren’t as demanding. It is used in circuits that are fully optimized to reduce production costs. It is limited to high-temp processes due to its lower thermal resistance. Some use cases include: Wearables, disposable electronics, and low-power sensors
Key Benefits:
⦁ Good dielectric properties
⦁ Lower moisture absorption
⦁ High-volume applications with low stress can be cost-effective
1.3 Teflon (PTFE) and LCP(Liquid Crystal Polymer)
Although PTFE is the priciest dielectric substance, its qualities are the best. It is used for niche applications that require high-frequency signal integrity and extreme chemical resistance. Most commonly in medical implants, research, aerospace, and military applications. In the first section, a table compares all properties of the two other materials.
2. Adhesive System: Bonding the layers
The adhesive is used to adhere the copper foil and the substrate, as well as to attach the coverlay and stiffeners. Not only does the choice of adhesive impact adhesion, but also flexibility and temperature stability. There are three types of adhesives/methods that are commonly used to bond:
⦁Acrylic Adhesives
⦁Epoxy Adhesives
⦁Adhesiveless Constructions
2.1 Acrylic Adhesives
Acrylic adhesives can be thermoplastic or thermosetting adhesives that are based on acrylic polymers. They are used in flexible PCB production to bond copper foils to polyimide and polyester substrates. They are used for general-purpose FlexPCBs, both in consumer and industrial products. However, they are prone to outgassing. They may also absorb moisture with time. Here are a few of the main advantages:
⦁Outstanding adhesion and flexibility
⦁Thermal endurance of up to 150 °C
2.2 Epoxy Adhesives
These products are ideal for situations requiring high chemical and thermal durability. They have excellent bonding properties. They are ideal for difficult environments because they can tolerate temperatures of up to 180 degrees Celsius. Among the main advantages are:
⦁Acrylic is more thermally stable.
⦁Resistant to solvents and chemicals
2.3 Adhesiveless Structures
Manufacturers use adhesiveless base films in some applications that require high reliability. This process involves laminating copper directly on the substrate by casting or sputtering. These methods are expensive but highly accurate. They are used for high-density PCBs with component pads of low pitch. Benefits include:
⦁Thinner Construction
⦁Improved dimensional stability
⦁Improved signal integrity on high-speed circuits
3. Protective Coatings: Coverlays & Overlays
Coverlays are protective layers that shield and insulate copper circuitry against environmental damage. Coverlays are often used instead of solder masks on flex PCBs. Coverlay coatings are available in two types:
⦁Polyimide Coverlay + Adhesive
⦁Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPI)
3.1 Polyimide Coverlay + Adhesive
The film is pre-coated in adhesive and provides excellent mechanical strength. It can withstand repeated stretching without cracking.
3.2 Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPI)
The LPI is similar in appearance to the solder masks used on rigid PCBs, but it has been adapted for FlexPCBs. It is compatible with automated PCB production and is easy to apply to pine pitch components.
4. Other considerations in material selection
4.1 Thermal Requirements
Choose a substance that can tolerate prolonged exposure to high temperatures and thermal cycling. In general, polyimide and epoxy systems perform well in these conditions.
4.2 The Mechanical Flexing
FPC’s flex time and cycle are important; dynamic-flex applications need thin, highly flexible substrates. Static-flex designs are best suited to thicker constructions.
4.3 Electrical Performance
Choose a material that has low dielectric loss for applications requiring high speeds and signal integrity. Low-dielectric constant material like PTFE is ideal for high-frequency and impedance controlled designs.
A One-Stop Shop for Affordable PCBs of High Quality
5. summary
Flex PCBs are not designed with a single material. Flexibility, thermal issues, and signal integrity are unique to each application. One of the most important tasks for an electronics engineer is to choose the best substrate, adhesive, and protective layer. Understanding the strengths and limits of different materials allows engineers to design Flex PCBs that not only meet but also exceed expectations for their intended uses.
If you want to design a Flex PCB, Assypcb provides high-quality PCB manufacturing, PCB assembly, and components sourcing services, as well as competitive prices.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China