A Complete Guide to Medical PCB Assembly
Table of Conent
Table of Conent
Let’s be honest, most people don’t think twice about what’s inside their smartwatch, insulin pump, or heart monitor. But here’s the thing: at the core of every medical device that saves lives or monitors health is something deceptively complex, medical PCB assembly.
Now, while your smartwatch might forgive a glitch or two, a pacemaker absolutely cannot. That’s the difference between general electronics and medical PCBA, there’s zero room for error. Every connection, every layer, every component must work flawlessly, often under extreme conditions.
In this complete guide, we’ll dive into the world of medical PCB assembly, break down how it works, what makes it so different, and why it’s become the backbone of modern healthcare. Whether you’re a designer, engineer, or just genuinely curious about how life-saving tech gets built, you’re in the right place.
1. What Is Medical PCB Assembly?
So, what exactly is medical PCB assembly?
At its core, it’s the process of assembling printed circuit boards, or PCBs, specifically designed for medical applications. These aren’t your typical PCBs slapped inside a toy drone or Bluetooth speaker. No, medical PCBA is held to the highest possible standard. We’re talking about boards that go into pacemakers, defibrillators, infusion pumps, medical imaging systems, and more.
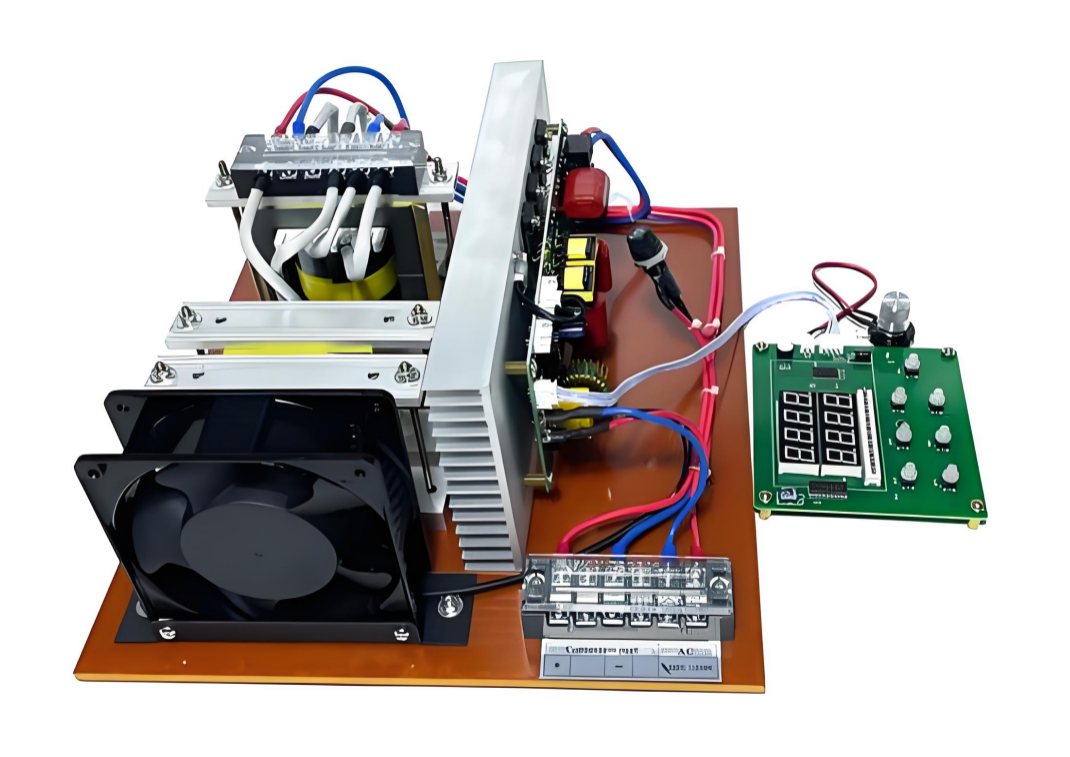
Think of them as the nerve center of every piece of high-stakes medical equipment. The performance of a pcba medical machine can literally make the difference between life and death. Because of that, medical PCB manufacturers must meet stricter regulatory requirements, more robust design standards, and achieve much higher reliability scores than their counterparts in consumer electronics.
And it’s not just about performance, it’s about long-term reliability, biocompatibility, and precision. These boards must endure sterilization, high-frequency vibrations, moisture, and sometimes even direct contact with the human body. So yes, medical PCBA is in a class of its own.
In short? This isn’t just assembly. It’s life-critical engineering, and it starts with the right process and the right mindset.
2. Critical Requirements for PCBA in Medical Devices
Now, before we get into how these boards are actually made, let’s look at what they absolutely must deliver.
First and foremost, any PCBA in a medical device must be safe. That means complying with strict standards like ISO 13485 and IPC Class 3, the highest level of quality for electronic assemblies. Devices can’t fail. Period. That’s why every medical pcba product is subject to rigorous inspection, both during and after assembly.
But safety is just the beginning. Reliability is equally important. Devices with embedded medical PCBA often run for years, sometimes decades, without a reset. These PCBs operate inside harsh environments, inside a human body, on ambulances, in MRI rooms, and so on. That’s why pcba medical machines need to handle extreme heat, cold, vibration, and more, all without missing a beat.
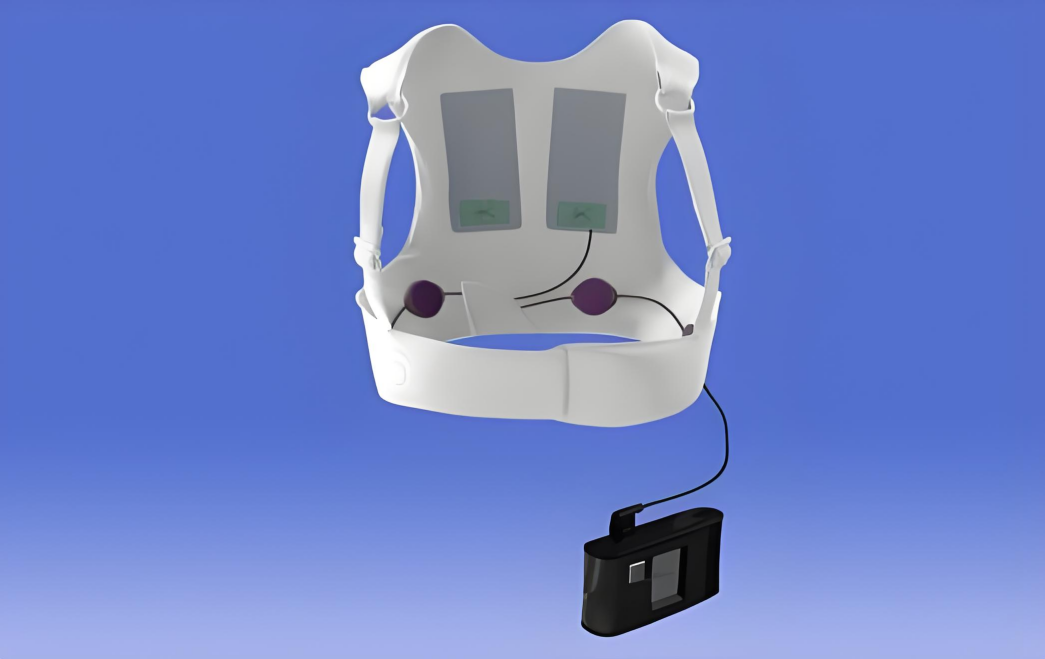
Then there’s size. Ever notice how modern medical equipment keeps getting smaller? That’s not a coincidence. Miniaturization is key, especially for wearable or implantable tech. It demands ultra-compact, densely packed medical PCB assemblies, often with complex multi-layer designs and advanced materials.
In a nutshell, the critical requirements boil down to this:
- Safety:No room for failure.
- Reliability:Years of stable operation, even in extreme conditions.
- Precision and miniaturization:Smaller boards, tighter tolerances, higher performance.
And here’s the twist: as demands keep increasing, medical PCB assembly services are evolving fast, but not every provider can keep up.
3. Types of Medical PCBs
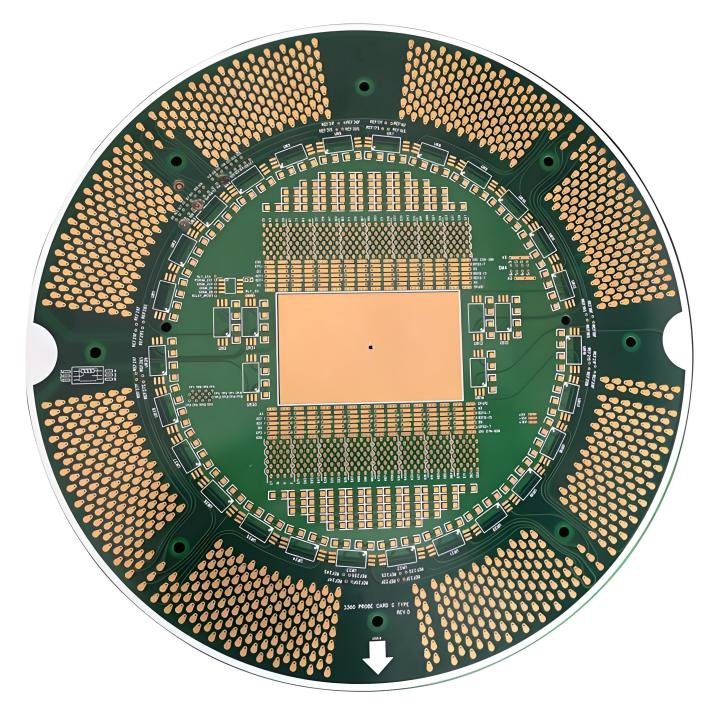
When it comes to designing electronics for healthcare, there’s no such thing as one-size-fits-all. That’s why medical PCB assembly spans across multiple board types, each tailored to specific medical environments, devices, and tolerances.
Let’s start with the basics: rigid PCBs, flex PCBs, and rigid-flex PCBs. These are the foundation of every medical electronics assembly, and each comes with its own strengths and limitations.
1) Rigid Medical PCBs
These are the standard go-to boards, firm, cost-effective, and stable. You’ll typically find rigid PCBs inside pcba medical machines like diagnostic equipment, imaging systems, and hospital monitors. They don’t bend or fold, but they’re reliable in large, stationary setups where space isn’t a constraint.
2) Flexible Medical PCBs
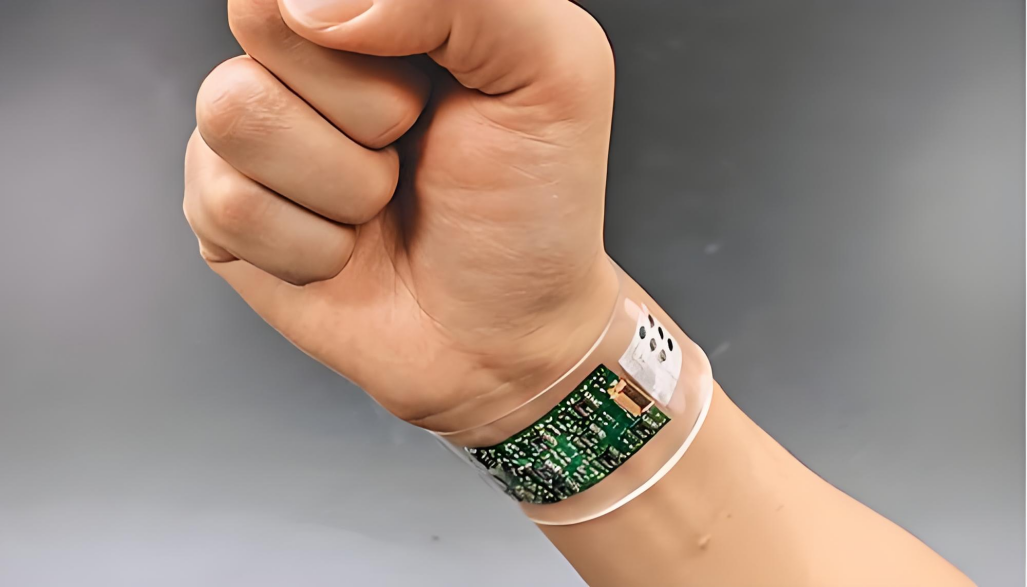

Now, if you’re working on something smaller, say a wearable glucose monitor or a PCBA in medical alert devices, you’re probably using a flexible PCB. These bendable boards are made to wrap around curves, fit into compact spaces, and withstand movement without breaking. The rise of medical device assembly for portable and wearable health tech is driving their demand sky-high.
3) Rigid-Flex Medical PCBs
Why choose between rigid or flex when you can get both? Rigid-flex PCBs combine solid board sections with bendable flex layers, making them ideal for medical pcba products that require both durability and flexibility, such as surgical instruments or implantable devices. You get the structural stability of a rigid board with the adaptability of a flex circuit. That’s a win-win in the operating room.
And let’s not forget the multi-layer and HDI (High Density Interconnect) options. With devices shrinking every year, these technologies let engineers pack more functionality into smaller, lighter PCBs, without sacrificing performance or safety.
In short, whether it’s a large-scale pcba medical machine or a skin-adhered wearable, there’s a specialized PCB type built for it. And choosing the right one? That’s step one in getting your medical pcb assembly service off on the right foot.
4. The Medical PCB Assembly Process

So, how do we actually build one of these things?
Well, unlike standard electronics, the medical PCB assembly process is less of a “factory routine” and more of a high-stakes precision dance. Every step is dialed in to meet strict tolerances and medical-grade expectations. Let’s break it down.
Step 1: Design & DFM (Design for Manufacturability)
Everything starts here. If the layout doesn’t account for real-world stress, heat, or size constraints, the rest of the process is doomed. A good medical pcb assembly manufacturer will review your design, catch any red flags, and make sure it’s ready for production before touching a single component.
Step 2: Component Sourcing
This part’s critical. Components used in medical pcba service must meet strict standards, both in terms of quality and traceability. Subpar parts are simply not an option. Many medical PCB manufacturers only work with vetted, certified suppliers to ensure every capacitor, resistor, and chip is compliant and reliable.
Step 3: SMT & Through-Hole Assembly
Once everything’s ready, the actual placement begins. SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is the go-to for most devices, but some products still require through-hole assembly, especially if they need mechanical strength or component height. Either way, medical pcb assembly demands controlled reflow temperatures, minimal solder defects, and absolute precision.
Step 4: Testing & Inspection
Testing isn’t optional here, it’s mission-critical. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), In-Circuit Testing (ICT), X-ray analysis, and sometimes even functional tests are standard protocol. After all, a single bad solder joint in a PCBA in red light therapy devices or a medical implant could be catastrophic.
Step 5: Final Assembly and Box Build
Lastly, everything is enclosed, labeled, and packaged, often in sterile conditions, depending on the application. This stage of the medical device assembly process ensures the PCBA is protected, fully integrated, and ready to be installed into its final housing.
Throughout every step, documentation and traceability are key. You need to be able to trace every board, component, and test result. That’s what separates a regular electronics vendor from a serious medical pcb assembly service provider.
5. Specialized Use Cases (Where Medical PCBA Makes the Difference)
The term medical PCB assembly might sound clinical, but the impact it has on everyday health is personal, even life-changing. These assemblies are embedded in the very tools we rely on for early diagnosis, chronic condition monitoring, and emergency interventions. Let’s dig into a few real-world examples where medical PCBA products are absolutely critical:
1) Red Light Therapy Devices
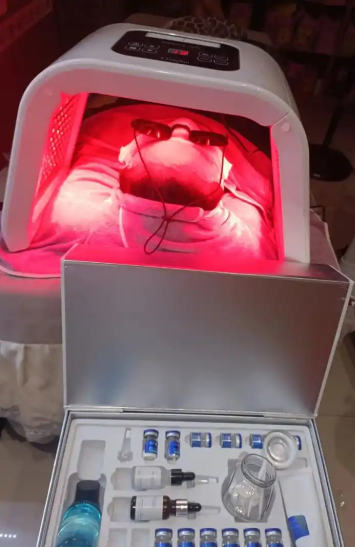
Often used for skin treatments, pain relief, or muscle recovery, these devices require PCBA in red light therapy devices that can manage high heat while remaining compact. The boards need excellent thermal tolerance, stable voltage control, and longevity, especially for at-home consumer models that may run daily.
2) Medical Alert Devices
These include fall detectors, panic buttons, and heart monitoring wearables. They usually operate wirelessly and must process and transmit data in real-time. PCBA in medical alert devices is engineered for lightweight wearability, long battery life, and rugged reliability, think elderly patients or individuals with disabilities who depend on them 24/7.
3) Portable Diagnostic Equipment
Blood glucose monitors, digital thermometers, and handheld ECG machines all use tightly packed medical PCBA to deliver hospital-grade accuracy in a home-friendly package.
4) Surgical Tools & Robotic Systems
Behind every beeping monitor or surgical robot arm is a custom pcba medical machine that’s been built to survive sterilization, shock, and constant use. These aren’t just PCBs, they’re precision-controlled lifelines.
In every case, the medical electronics assembly is more than just a platform for components. It’s the brain behind the care.
6. Choosing the Right Medical PCBA Manufacturer
Finding the right medical PCB assembly manufacturer is a bit like hiring a heart surgeon. You need precision, certification, transparency, and absolutely no shortcuts. Whether you’re sourcing locally or abroad, these are the criteria that separate trustworthy medical PCBA service providers from the rest.
Comparison Table: What to Look For
| Feature | Good Manufacturer | Bad Manufacturer |
| Certifications | ISO 13485, IPC Class 3, FDA, RoHS | Missing or vague compliance claims |
| Design Feedback | Offers DFM input, flags layout risks | Accepts files blindly, no feedback |
| Testing | AOI, X-ray, ICT, functional tests | Visual inspection only |
| Communication | Responsive, transparent, clear quotes | Delayed, templated, evasive replies |
| Sample Validation | Shares test data and revision logs | No data, “take-it-or-leave-it” samples |
| Packaging & Shipping | Cleanroom, ESD-safe, traceable packaging | Generic, untraceable packaging |
Choosing wrong means risking delayed timelines, failed units, or worse, safety concerns in live devices. Always vet aggressively before you commit.
7. Why So Many Medical PCBs Are Assembled in China
It’s no secret, China is the global hub for electronics manufacturing. But when it comes to medical PCB assembly, the lead isn’t just about cost. It’s about infrastructure, experience, and scale.
Why China Dominates: Quick Comparison
| Factor | China | Other Regions |
| Production Volume | High (1000s of units per day) | Moderate to low |
| Speed to Market | Rapid prototyping & shipping | Slower lead times |
| Advanced Equipment | Widespread SMT automation, 3D AOI, X-ray | Varies greatly |
| Labor Cost | Low-to-mid range with skilled operators | Higher cost overall |
| Material Sourcing | Domestic component access, fast procurement | Often imported |
| Vendor Options | Dozens of reliable medical pcb manufacturers | Fewer niche specialists |
But, and this is key, not all Chinese providers are equal. Some focus purely on volume, cutting corners to underbid competitors. That’s why it’s critical to look beyond price.
Here’s what you should ask upfront:
- Do they have past experience with medical pcba service?
- Can they support traceability and documentation?
- Will they guide you through DFM before fabrication?
If they can’t say yes to all three, keep shopping.
8. Common Pitfalls in Medical PCB Assembly
Even with the right partner and solid design files, mistakes happen, and in the world of medical PCB assembly, small mistakes become massive liabilities.
Here are the biggest traps:
1) Poor Heat Dissipation
Devices like pcba medical machines generate constant heat. If copper traces are too narrow or thermal relief isn’t built into the design, components overheat, and patients suffer.
2) Sharp Trace Angles
Those neat-looking 90° turns? They’re stress concentrators. Flexible boards especially (common in medical alert devices) need gently curved traces to prevent cracking.
3) Vias and Pads in Bend Areas
This one’s a classic mistake. Put a via in a flex zone and you’re asking for delamination. Every competent medical pcb assembly service knows to avoid this, but many budget providers don’t.
4) Loose Assembly Standards
If your board isn’t IPC Class 3, it’s not medical-grade. End of story. Always confirm your medical pcb assembly manufacturer builds to this standard.
Avoiding these problems isn’t about luck, it’s about process. And the better the process, the longer your product will work where it matters most.
9. Quality Control: The Quiet Hero of Medical PCBA

Let’s say your design is flawless. Your assembly partner did a great job. What could still go wrong?
Plenty, unless quality control is built into every layer.
Here’s what elite-level medical PCB manufacturers implement by default:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) after every reflow
- In-Circuit Testing (ICT) to confirm connectivity and resistance levels
- Functional Testing that mimics real-world operation
- Burn-in Testing for products expected to run nonstop
And most importantly?
Traceability Logs. Every board should come with batch history, lot numbers for components, test results, and visual evidence. If a unit fails in the field, you need to know why, instantly.
This level of accountability isn’t optional. It’s what separates medical PCBA from the hobbyist world.
10. What’s Next for Medical PCB Assembly?
We’re standing at the edge of something big. As electronics shrink, and AI powers more decision-making in hospitals, medical PCBA is transforming fast.
Trends You Can’t Ignore:
- AI in Manufacturing: Real-time inspection tools now use AI to detect defects before they happen.
- Implantables: Think flex PCBs embedded in the body, monitoring, regulating, even delivering medication.
- Smarter Wearables: ECG patches, glucose sensors, and fertility trackers with rigid-flex PCBs are going mainstream.
- Material Innovation: From stretchable copper to bioresorbable polymers, medical electronics assembly is turning science fiction into product specs.
Bottom line? The best medical pcb assembly services aren’t just reacting, they’re innovating. And if your supplier isn’t evolving with the tech? You’ll get left behind.
11. Medical PCBA FAQs
12. Summary
By now, one thing should be clear: medical PCB assembly isn’t just another line on a BOM or a step in device production. It’s the heart of modern healthcare technology, and it demands precision, reliability, and deep technical know-how.
From PCBA in medical devices like surgical robots and heart monitors, to wearables and portable diagnostics, the role of the medical PCB assembly service is only growing. As technology advances, expectations follow. Smaller boards. Tighter tolerances. Smarter systems. And absolutely zero tolerance for failure.
Whether you’re designing a medical pcba product for red light therapy or choosing a medical PCB assembly manufacturer to deliver your next generation alert device, the key is to partner wisely, design carefully, and test relentlessly.
Because in healthcare, there are no second chances, and your PCBA needs to work the first time, every time.
Want to learn more or request a quote?
Visit https://assypcb.com, your one-stop solution for medical PCB manufacturing, component sourcing, and top-tier medical PCBA service.
Latest Blog
Contact Info
Phone: +86-755-82882936
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: +86-13570802455
Wechat: +86-13570802455
Address: 2nd floor,D Bldg.,Electric Link Technology Bldg.,Gongming,Guangming New Dist.,518106 Shenzhen, China