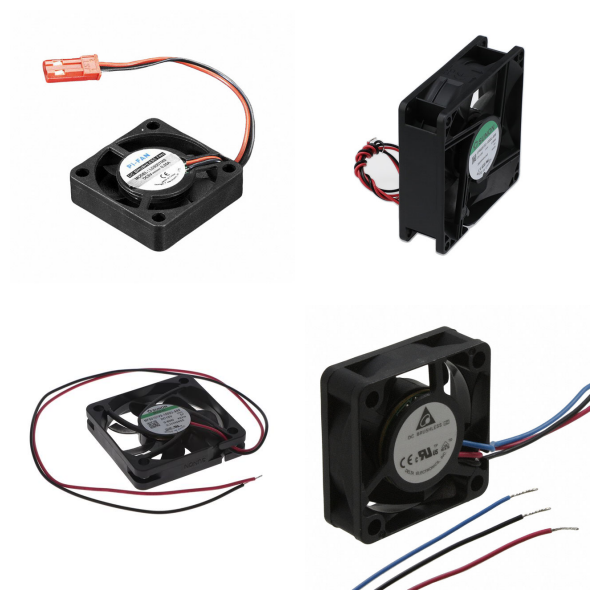
Fans
1. Fans Overview
1) Function Positioning
Fans usually refer to cooling fans, which are key components for auxiliary heat dissipation management in electronic devices. Its core function is to reduce the operating temperature of high-power components (such as CPU, GPU, power module, etc.) through forced convection to ensure system stability.
2) Technical Classification
By Driving Mode: It can be divided into DC fans and AC fans. DC fans are more suitable for consumer electronics due to their small size and low power consumption.
By Control Mode: It includes constant speed fans, PWM speed control fans and intelligent temperature control fans. The latter adjusts the speed in real-time through sensors to balance heat dissipation efficiency and noise.
2. What are the Core Parameters of Fans?
1) Key Performance Indicators
Air Volume (CFM): directly affects the heat dissipation capacity and needs to be matched according to the heat generation of the equipment;
Noise (dB): positively correlated with the speed, and low noise design is preferred for precision equipment;
Power Consumption and Life: The bearing type (oil/ball bearing) significantly affects durability.
2) Application Adaptation Principle
Industrial scenarios focus on high air volume and high-temperature resistance, such as server rooms;
Consumer electronics (such as laptops) prioritize compact design and silent performance.
3. What are Fans Used for?
Electronic System
In smartphones, micro fans are used in heat dissipation modules, and graphene heat conductive sheets are used to achieve efficient thermal management;
In the automotive electronics field, high-power fans are used for battery cooling systems and car charger heat dissipation.
Maintenance and Optimization
Regular cleaning of fan blade dust can avoid performance degradation caused by increased wind resistance;
Combined with temperature monitoring circuit design, dynamic optimization of fan start and stop logic is achieved.
4. Technology Development Trends of Fans
The integration of IoT and AI technologies promotes the development of fans towards intelligent and integrated, for example:
Smart fans achieve fault pre-diagnosis through embedded sensors;
Brushless motor technology improves energy efficiency and adapts to the needs of green energy equipment.
5. Fans FAQs
1) What is the main function of the cooling fan in the circuit?
It is used to reduce the temperature of electronic equipment and prevent performance degradation or damage to components due to overheating. It is commonly used in power modules, CPU cooling, and other scenarios. Its control circuit is often linked with a temperature sensor (such as a thermistor) to achieve dynamic speed regulation.
2) What key components are needed to drive the fan?
Switching Elements: such as MOSFET or triode, used to control the start,stop and speed of the fan.
Protection Elements: fuse (overcurrent protection), TVS diode (voltage surge protection), etc.
3) How to choose a suitable cooling fan?
Electrical Parameters: match the rated voltage and current of the equipment, and consider the driving ability of the power amplifier element.
Environmental Factors: the size and bearing type (such as ball bearings have a longer life) should be selected in combination with the cooling requirements (air volume, noise).
4) How to optimize the energy consumption of the fan?
Dynamically adjust the speed through the PWM control algorithm to reduce the standby power consumption; or use a low-power switching power supply module for power supply.
5) Possible reasons why the cooling fan does not rotate?
Circuit Failure: the driving triode is damaged and the fuse is blown.
Mechanical Problem: Bearings are stuck or have too much dust, so they need to be cleaned and lubricated regularly.
6) How to reduce fan noise?
Hardware Optimization: Choose silent bearings or add rubber shock-absorbing pads;
Software Control: Optimize the frequency of PWM signals to reduce resonance.
7) How to implement fan control in a typical circuit?
Take CPU cooling as an example: A temperature sensor (such as a thermistor) detects temperature → signal is processed by an operational amplifier → PWM signal output is controlled → field effect tube is driven to adjust fan speed.