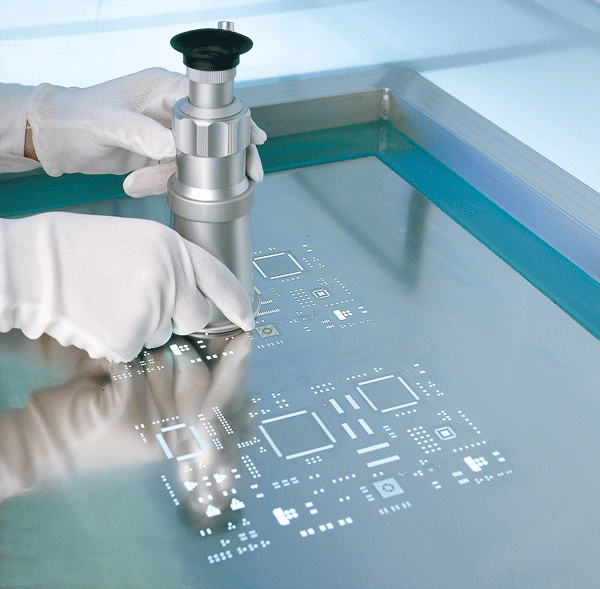
PCB stencils are metal plates with precisely cut openings. They have a very unique design. They make it possible for adhesives and solder paste to flow through the holes. Their only function is to
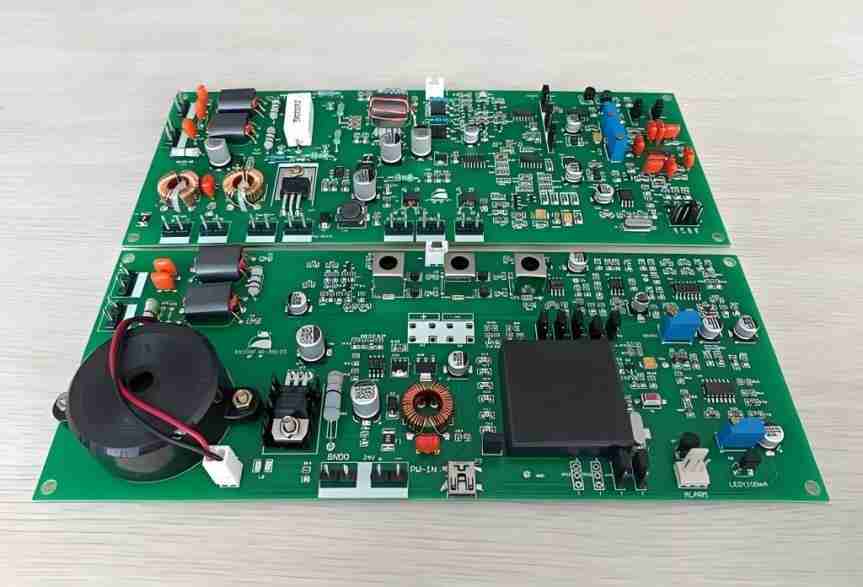
A printed circuit board's component arrangement and electrical connections are referred to as the assembled circuit board layout. In essence, it is a map that indicates the locations of each component and how electrical
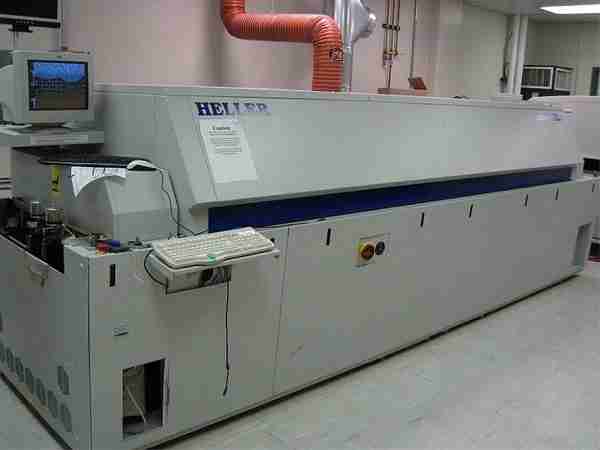
One common technique for making SMT complete circuit boards is reflow soldering. The PCB that the components will be positioned on is covered with solder paste. Solder paste is applied to the PCB card on
COB LED, Chip On Board LED boards represent a category of high-power LED light sources. These boards possess the capacity to encapsulate multiple LED chips on a singular aluminum substrate. The configuration of the COB
As technology advances, many innovations are being introduced around the world. You can now see glass assembled circuit board being used in the circuit industry. You must be wondering now why it is necessary
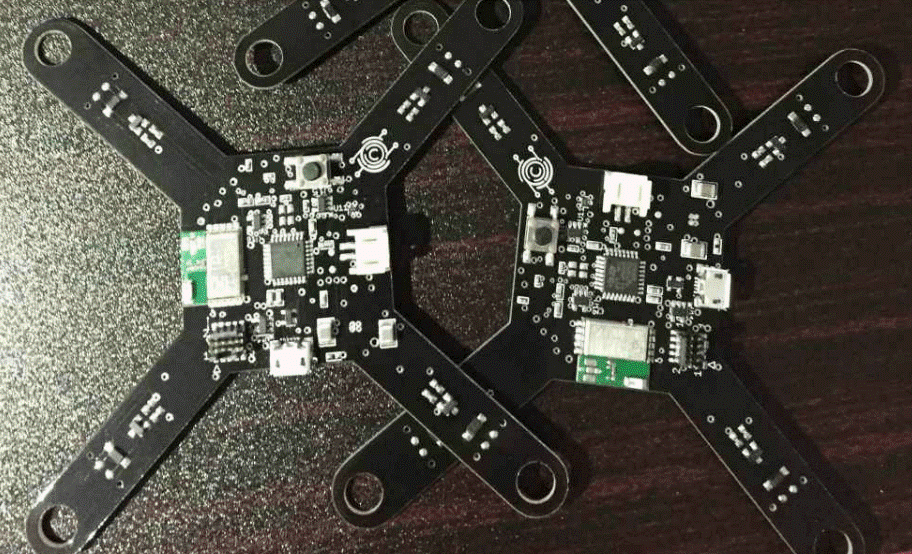
The Drone PCB, a type of printed circuit board that is used in drone technology, is the brain. A flat, insulating sheet with conductive paths connecting electronic components. FR-4 laminates are flexible and durable, reinforced with glass
Cavity printed circuit boards are high-performance boards featuring a unique cavity shape. Their recessed area enables more efficient use of space, which in turn enables consolidation and miniaturization of components such as microcontrollers and heat
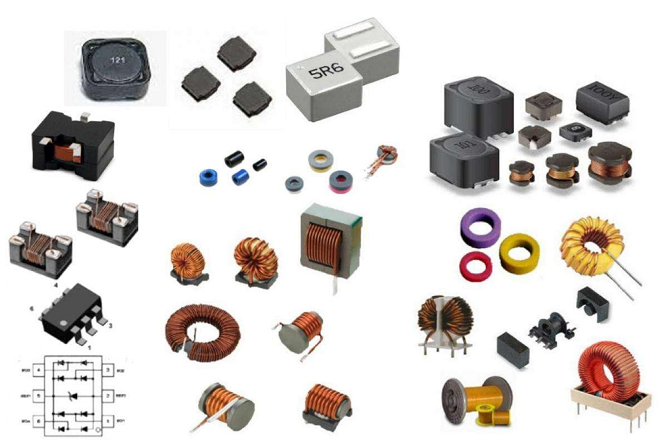
Every electronic device is made up of electronic components.To successfully complete any task, it is important to understand the components that compose an electronic system. Electronic components like resistors, diodes, and capacitors are used across
Mobile PCI Express Module (MXM) is a set device interfaces that are based on PCI-Express for graphics processors and targeted to different types of notebooks. This not only allows for a shorter product development
Are RF assemblies low-frequency or high-frequency? The operating frequency of RF components may range from very low frequencies up to extremely high frequencies. The RF range is 3kHz up to 300GHz. In practice however, the
Email us for a Free Quote: [email protected]